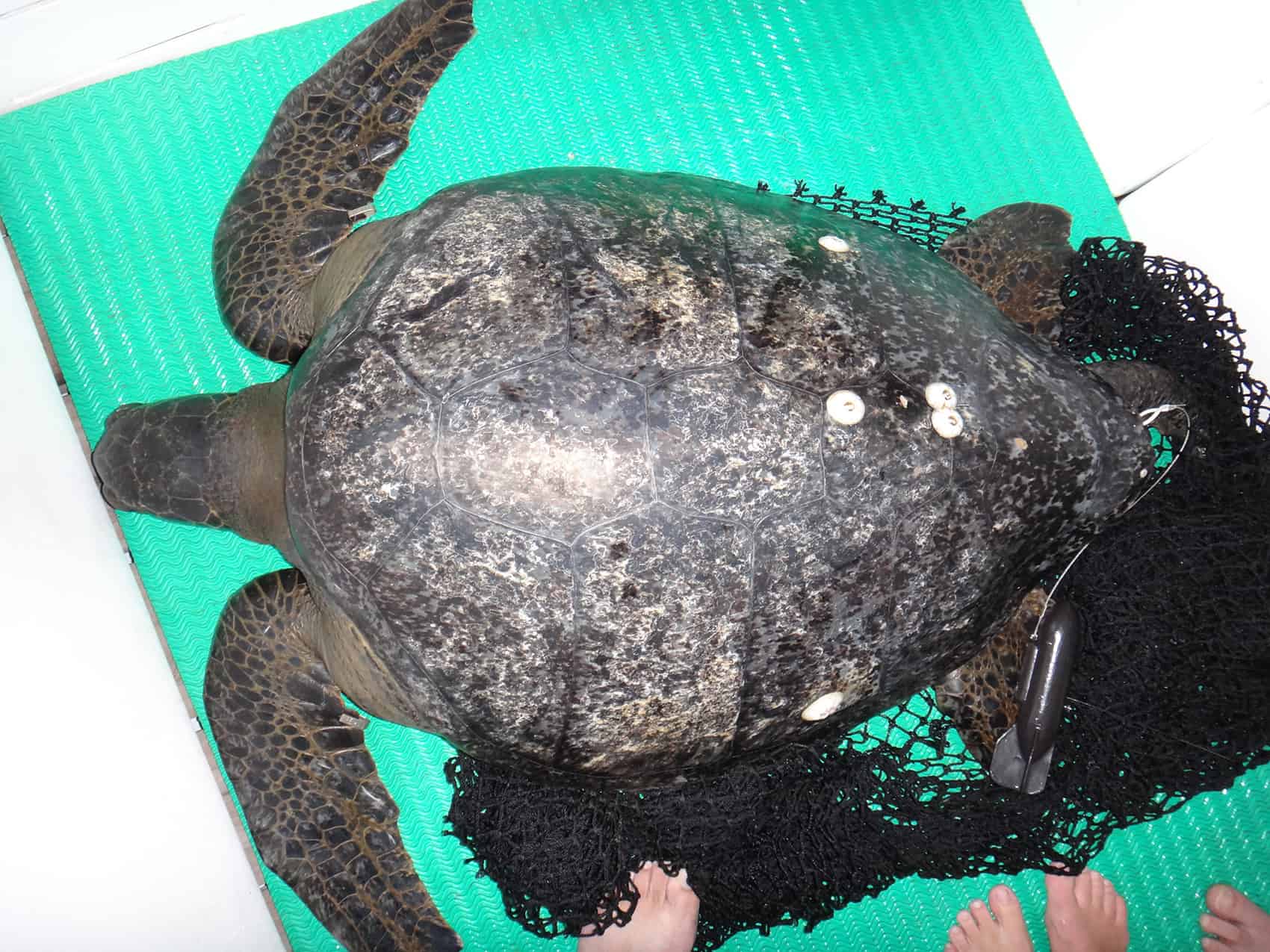
One normal migration for turtles, one giant discovery for humankind.
With his 14-day journey from the waters of Costa Rica’s Cocos Island National Park to the Galapagos Marine Reserve in Ecuador, “Sanjay,” an endangered green sea turtle, established the first direct migration link between the two protected areas.
Sanjay was one of three green sea turtles tagged by scientists from the marine conservation groups Turtle Island Restoration Network and PRETOMA during a 10-day research expedition. Using a $4,000 satellite tag, biologists from the organizations were able to map Sanjay’s exact migration.
“It’s truly remarkable. Sanjay knew where he was headed, and made a beeline from one marine protected area to the next,” said Alex Hearn, conservation science director for Turtle Island Restoration Network. “These protected areas of ocean are hot spots for endangered green sea turtles, but we also need to think about their migratory corridors between protected areas.”
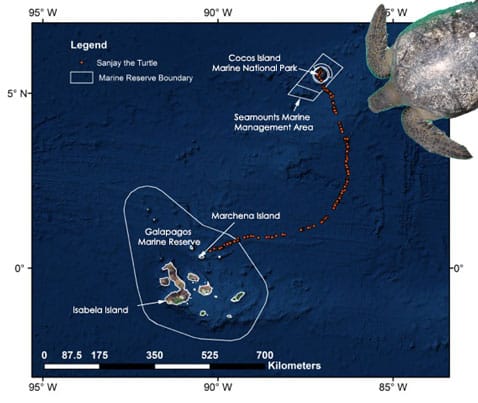
Though the two organizations have tagged hundreds of sea turtles over the years, Sanjay is the first to show movement between the two protected areas. Sanjay’s migration is the latest piece of evidence linking the green turtles of the Galapagos and Cocos Island, a link that biologists have long suspected due to the populations’ genetic similarities.
The project’s researchers hope that the new evidence will help encourage the development of conservation programs between protected areas.
“These species are protected while they are in the reserves, but as soon as they swim beyond the no-fishing zone, they are being hammered by industrial fishing vessels that set millions of hooks in the region,” said Todd Steiner, executive director of Turtle Island Restoration Network. “Our goal is to collect the necessary scientific data to understand the migratory routes and advocate for ‘protected swimways’ to protect these endangered species though out their migration.”
Watch Sanjay’s release into the ocean near Cocos Island