WASHINGTON, D.C. – Here’s a pretty astonishing chart on the skyrocketing number of arrests in the United States of African Americans for nonviolent drug crimes.
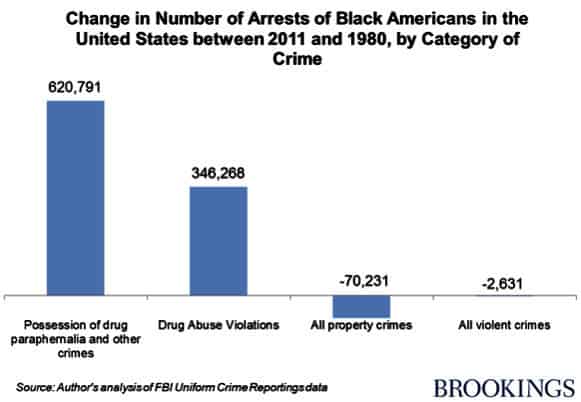
Brookings’ Jonathan Rothwell lays it out:
Arrest data show a striking trend: arrests of blacks have fallen for violent and property crimes, but soared for drug related crimes. As of 2011, drug crimes comprised 14 percent of all arrests and a miscellaneous category that includes “drug paraphernalia” possession comprised an additional 31 percent of all arrests. Just 6 percent and 14 percent of arrests were for violent and property crimes, respectively.
Even more surprising is what gets left out of the chart: Blacks are far more likely to be arrested for selling or possessing drugs than whites, even though whites use drugs at the same rate. And whites are actually more likely to sell drugs:
Whites were about 45 percent more likely than blacks to sell drugs in 1980, according to an analysis of the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth by economist Robert Fairlie. This was consistent with a 1989 survey of youth in Boston. My own analysis of data from the 2012 National Survey on Drug Use and Health shows that 6.6 percent of white adolescents and young adults (aged 12 to 25) sold drugs, compared to just 5.0 percent of blacks (a 32 percent difference).
This partly reflects racial differences in the drug markets in black and white communities. In poor black neighborhoods, drugs tend to be sold outdoors, in the open. In white neighborhoods, by contrast, drug transactions typically happen indoors, often between friends and acquaintances. If you sell drugs outside, you’re much more likely to get caught. Rothwell’s numbers shoot some holes into some oft-repeated drug warrior talking points: that people don’t get arrested for nonviolent drug crime as much as they used to (false), and that legalizing and decriminalizing certain drugs won’t magically solve racial disparities in the criminal justice system (true, although the chart above suggests it could help).
Ingraham is a data journalist focusing primarily on issues of politics, policy and economics. He previously worked at the Brookings Institution and the Pew Research Center.
© 2014, The Washington Post






